The World Health Organization (WHO) in 2017 published a report showing serious concerns about new drug developments and antibiotic discovery under clinical trials or antibiotic development pipeline.
WHO
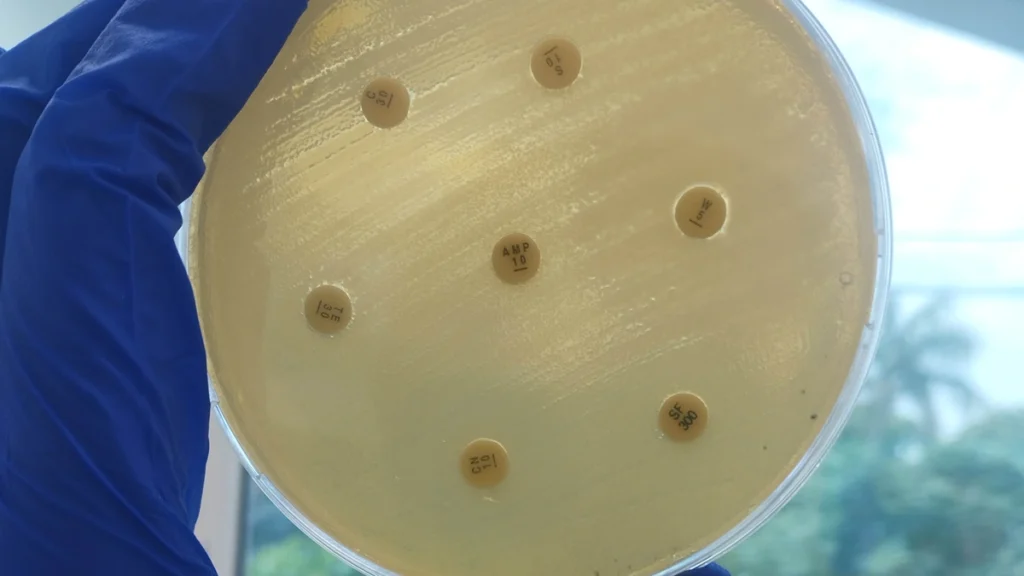
New drug developments are the need of time due to rapidly spreading drug resistance bacteria but new antibiotics pipeline has fewer drugs which are not sufficient for future need for the treatment of drug resistance bacteria. WHO report identifies that there are only 51 new antibiotic drugs and biologicals in antibiotic development pipeline for treatment of priority antibiotic-resistant pathogens as per WHO classification which includes Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Clostridium difficile.
However, only eight out of fifty one drugs are found as truly innovative due to difficulties in research and development of new antibiotics. With the success rate of 14% from phase I trials to approval, it is expected that only 10 drugs will become commercial within 10 years while only one or two are effective against Gram-negative bacteria.
Why new drug developments and antibiotic discovery is important?
Antibiotic resistance is a looming crisis and raised concerns of clinicians, researchers, policymakers, politicians and the public at large. Rapid emergence and widespread distribution of antibiotic resistance in critically important and deadly bacterial pathogens has made easily treatable bacterial diseases deadly again.
Nowadays, there are few novel antibiotic drugs under n ew drug developments in new antibiotics pipeline while antibiotic resistant bacteria are rising rapidly making available antibiotic drugs ineffective. Therefore, it is important to develop a strategy to control antimicrobial resistance and emphasize on new drug discovery to avoid major public health problem.
The golden era of antibiotic discovery 1940 – 1962:
Historically, majority of the currently available antibiotic drug classes were discovered and introduced to the market during the golden era of antibiotic discovery. Each antibiotic drug class typically contains several antibiotic drugs discovered during this era and then their modified versions also synthesized to treat different diseases. For example, numerous β-lactams drugs such as different penicillin’s and cephalosporins.
What are the currently available antibiotics drugs?
Nowadays the most prevalent antibiotics available are
- Amoxicillin
- Ciprofloxacin
- Azithromycin
- Cephalexin
- Levofloxacin
- Tobramycin
- Tigecycline
- Fosfomycin
- Moxifloxacin
- Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole and
- Amoxicillin/clavulanic acid
As a last line of defense, humanity has
- Vancomycin and its analogue telavancin
- Amikacin
- Linezolid
- Colistin (polymyxin E), and
- Amphotericin B (an antifungal agent).
Why few antibiotics are under development?
Unfortunately, the new drug developments are being done at lower pace while the antibiotic resistance is emerging at higher pace. Below mentioned are few reasons or difficulties in the way of new drug discovery faced by scientists and pharmaceutical companies.

- Scientific or technical hurdles:
New drug developments is extremely difficult due to pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamics of a substance along with low toxicity to host cell and high toxicity to bacterial cell. Efforts in new drug developments fail due to lack of target to unique target site only found in bacteria so that it only kills bacteria and does not harm the patient.
Many of these antibiotic drugs currently available were originally isolated from natural products in soil microbes. Because it is difficult to grow microbes of external environment in laboratory therefore, new bacterial isolation-methods can re-open the possibility of new drug developments. For example, new method to grow soil bacteria allowed scientists to grow 50% soil bacteria as compared to 1% as a result; they discovered teixobactin that targets Gram-positive bacteria (like MRSA)
- Financial or regulatory issues:
new drug developments are very expensive because every formulation or chemical compound has to go through rigorous testing for activity and patient safety while only few successfully pass through the entire new drug developments process. Moreover, the complete drug testing process is time taking and takes tens of years to complete however, antibiotic resistance against the antibiotic emerges rapidly.
Can new antibiotic drug discovery solve antibiotic resistance problem?
The looming threat of antibiotic resistance cannot be solved by new drug developments and antibiotic discovery of one or a few new antibiotic drugs because bacteria will eventually become resistant to any antibiotic however; it can be managed by prudent use of antibiotics. Whenever a new antibiotic drug reaches in market, it should be preserved and used responsibly otherwise it will become ineffective due to development of bacterial resistant against the drug.
It is important to learn from previous mistakes and concrete steps should be taken to slow down the process of antibacterial resistance. In the long run, health authorities and pharmaceutical companies must find alternative ways to prevent, control and treat bacterial infections and they should not rely solely on discovery and development of antibiotics.
